APPLICATION OF QUANTITATIVE DATA ANALYSIS IN FINANCE
INTRODUCTION
Quantitative data is a collection of numerical data mostly utilized in business standards for analytical and statistical purposes. It can be effectively adjusted and managed in financial sectors, especially to avoid manual and common financial mistakes. In recent decades, the participation of different new technologies, such as Artificial Intelligence, has been a goon for many time-consuming business difficulties. Governments use QA to make monetary and other economic policy choices. Governments and central banks of Singapore, Malaysia, Australia, Germany, Canada frequently track and assess statistical data, like GDP and employment numbers, as part of QA. [1]
QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS IN FINANCE:
Quantitative analysis is a strategy for understanding behaviour that employs mathematical and statistical modelling, measurement, and investigation. It is used for measuring, evaluating, and valuing financial products and forecasting real-world events such as changes in a country’s GDP.
QA is used in the financial services sector to assess investment possibilities, such as buying or selling assets. When making investment decisions (e.g., whether to purchase shares of a company’s stock), investors use crucial financial measures such as the price-earnings ratio (P/E) or earnings per share (EPS).
Due to a lack of different modern technologies in previous decades, the financial sectors have faced several problems, resulting in significant issues in the organization’s economic position, household budgets, and national revenue. Quantitative analysis is the act of obtaining and analyzing measurable and verifiable data like revenues, market shares, and wages to understand human behaviour better. [2] Some of the recent quantitative analysis techniques for finance are:
- Regression Analysis: Regression analysis may be used to determine how interest rates affect the behaviour of customers who invest in assets. Determining the influence of credentials and employment experience on yearly wages is another major use of regression analysis.
- Linear programming: It is a mathematical method for deciding how to get such a perfect answer. It is frequently used to determine if a company can maximize sales while minimizing operating expenses given a set of restrictions such as labour.
- Data Mining: Data mining is a set of skills that combines computer programming and analytical methods. The popularity of data mining is growing in lockstep with the amount and size of available data sets. Data mining technologies are used to analyze extraordinarily large amounts of data to find hidden patterns or relationships.
These three are the common quantitative data analytic techniques that provide huge support in finance. To estimate the issues of the financial sector and provide more accuracy and reliability.
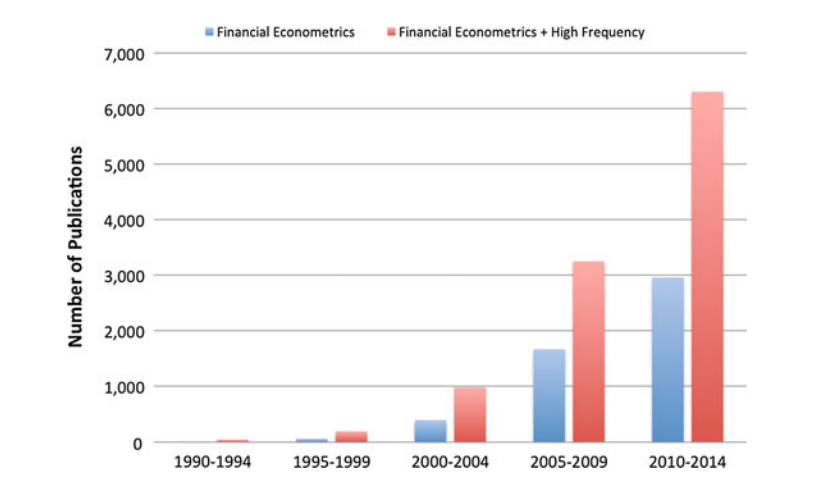
FIGURE 1: Number of publications related to high-frequency econometrics on Google Scholar [2]
APPLICATION OF QUANTITATIVE DATA IN FINANCE:
When it comes to financial industries, the complicated repercussions confronted by CEOs in company organizations are to additional decision-making scenarios. To eliminate these complications, the business now adheres to quantitative analytics-based concepts. There are several applications in finance that are based on quantitative data.
DATA PROJECTION:
To anticipate future data, researchers use algorithms and quantitative analytic approaches. For example, a company preparing to promote will generally evaluate quantitative data from various studies to anticipate an increase or decrease in sales. [3]
ANNUAL INCOME:
When deciding the selling price of a product, an organization utilizes quantitative data on a person’s or household’s yearly income to determine purchasing power. This activity is part of the business research process and may be performed before introducing a new product or a price modification for an existing product.
CONSUMER SATISFACTION SURVEY:
This is an example of a company using statistical quantification of qualitative components to improve customer service. For example, asking a customer to rate a menu addition on a scale of 1-10 will help the restaurant decide whether to eliminate it, improve it, or keep it as is. [4]
TABLE 1
Machine learning and Data analytics Techniques and algorithms for finance: [5]
| S.NO | METHODS OR TOOLS | PURPOSE |
| 1. | Financial disclosure analysis | This is a process of reviewing and analyzing a company’s financial statements to make better economic decisions. |
| 2. | Blockchain technology | It is a system of recording information’s in a way to makes it difficult or impossible to change, hack or cheat the system. |
| 3. | Deep learning | It’s a subset of artificial intelligence’s machine learning that uses networks to learn data.. |
| 4. | CNN | CNN is a mapping technique between the input and the output |
| 5. | Machine learning | This is a study of computer algorithms that improve automatically through experience and by the use of data. |
| 6. | Bitcoin | It is the first digital decentralized cryptocurrency that has shown a significant increase in market capitalization in recent years. |
CONCLUSION
Quantitative analysis (QA) is an approach for understanding behavior that employs mathematical and statistical modeling, measurement, and research. Quantitative express reality as a numerical value. Quantitative analysis is used to evaluate financial instruments and forecast real-world events such as GDP fluctuations. [6]
REFERENCE
- Masson, Corentin, and Patrick Paroubek. “Nlp analytics in finance with more: A french 250m tokens corpus of corporate annual reports.” Proceedings of The 12th Language Resources and Evaluation Conference. 2020.
- Shi X., Zhang P., Khan S.U. (2017) Quantitative Data Analysis in Finance. In: Zomaya A., Sakr S. (eds) Handbook of Big Data Technologies. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-49340-4_21
- Loperfido, Nicola. “Kurtosis-based projection pursuit for outlier detection in financial time series.” The European Journal of Finance 26.2-3 (2020): 142-164.
- LUBIS, Adelina, et al. “The Effect of Corporate Communication and Service Quality on Customer Loyalty and Satisfaction in Sharia Banking.” The Journal of Asian Finance, Economics and Business 8.3 (2021): 1267-1274.
- Błaszczyński, Jerzy, et al. “Auto loan fraud detection using dominance-based rough set approach versus machine learning methods.” Expert Systems with Applications 163 (2021): 113740.
- Caruso, G., et al. “Cluster Analysis for mixed data: An application to credit risk evaluation.” Socio-Economic Planning Sciences 73 (2021): 100850.
