3 Most Important Challenges To Be Considered While Using Social Media Data For Medical & Healthcare Research
In Brief:
- Studies indicated that patients primarily used Twitter (59.9%), particularly for increasing knowledge and exchanging advice and Facebook (52.3%), particularly for social support and trading advice. Professionals mainly used LinkedIn (70.7%) and Twitter (51.2%), for communication with their colleagues and marketing details.
- As patients continue to turn to online means for health care information to monitor their decisions, it is becoming gradually significant for radiologists to involve with patients online via social media daises. There are several means that physicians can use social media to deliver patients with valued information and develop the complete patient experience. By elevating discoverability, curating radiology, involving with patient communities, and generating mineable social media content, radiologists can develop as thought leaders in this new form of patient-centered announcement and information discussion.
INTRODUCTION
Social media channels are being used by patients for switching health information, involvements with their chronic condition, and pursue information from other people or establishments, for example,
- NHS Choices ( www.nhs.uk)
- Joining the Conversation describes Big White Wall (www.bigwhitewall.com)
- Mental health SNS that facilitates peer-professional interactions
- National Institute for Health & Care Excellence (NICE)
- UK government (https://www.gov.uk/government/publications)
- NHS England Publication stores (www.healthline.com)
Given that there is a high usage of social media for exchanging health information, it offers new opportunities between and amongst healthcare professionals, patients and public. Data Analysis on Healthcare service information ‘empowers’ patients and the general public to make responsible decisions.

Today, publicly available real-world social media blogs, microblogs
internet forums, content communities [such as YouTube, Flickr], social networking sites [such as Facebook and LinkedIn), data can now be analyzed with relative ease, bypassing many logical challenges associated with traditional approaches of Data Collection (e.g. electronic medical records, or conventional randomized clinical trials). Despite the high flow of data, researchers have struggled with three essential challenges:
- Which is the most common disease category shared in public posts?
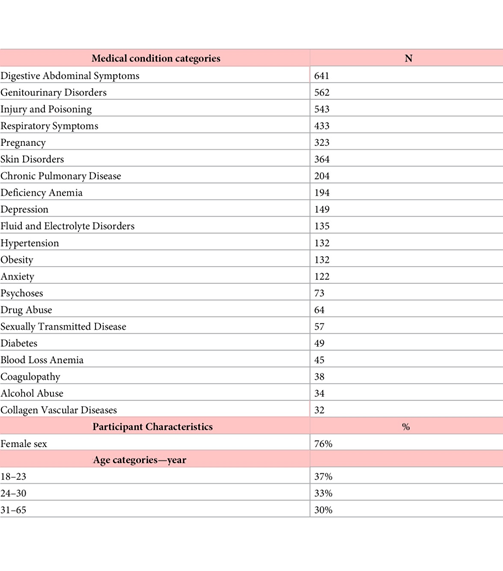
2. What kind of information can be extracted from Social networking sites?
Social media channels provide efficient, permeating and user-friendly daises that can inspire involvement, engagement and achievement required from both those who collect and deliver care to make health promotion interventions effective.
Participating health methods are progressively drawing consideration among the scientific community and could be used for health promotion programs through social media such as reviews, forum discussion, blogs, micro blogs and social networks. The time restraints of today’s medical practice pooled with the demand for chronic conditions make any additional request of extra time used by Health Care Experts a challenge.
3.What are ethical guidelines to be adopted for extracting and analyzing health behaviour?
According to the Fortune Report (March 18, 2019), the parliamentary group called on the social media platforms to give researchers all the Data Analyst they need to analyses the problem and the following the polluter pays principle – to pay a 0.5% levy on their profit to fund a “Social Media Health Alliance”.
- Study designs using social media-derived data should be transparent and readily available to the public.
- Researchers should respect the context in which content is sent.
- All data that can be used to recognize tweet authors, including geolocations, should be available.
- No information collected from social media should be used to procure more data about tweet authors from other sources.
- Study designs that necessitate Data Collection from a few personalities rather than combined analysis entail Institutional Review Board (IRB) approval.
- Researchers should adhere to a user’s attempt to control his or her data by respecting privacy settings.
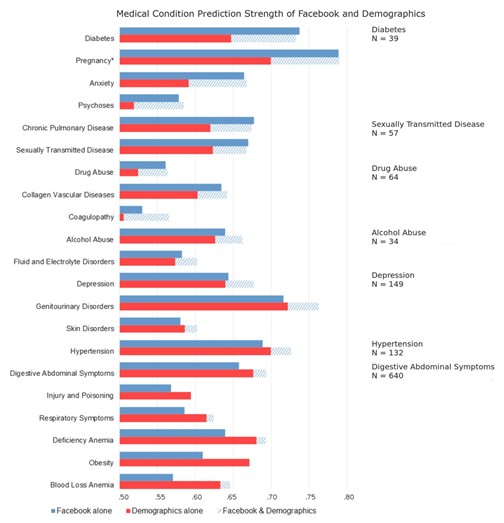
Social media applied in a healthcare context represent a tempting opportunity to improve the patients’ well-being, promoting patient care and education. The major Healthcare Social Networking (HSN) platforms require the massive action of a medical professional who replies to patient’s queries, also acting as moderators on specific topics when it is needed. Healthcare social networks present several benefits, including:
• Promoting networking and information exchange, enabling self-education among patients about particular diseases.
• Sharing patients’ experiences that can be helpful for other ones
• Supporting the treatment process
• Reducing the patient’s stress when he/she is waiting for a diagnosis or when he/she discovers to be affected by a particular disease
• Promoting information gathering and prevention campaign regarding specific diseases
• Optimizing the work of the clinical personnel who interact with patients skilled in their diseases
• Promoting knowledge management
• Promoting research and monitoring activities
Conclusion
Social media information has the benefit that it often has a built-in communication network back to patients. For example, Facebook now allows users to flag posts within their system that they think may suggest suicidal ideation. Facebook then anonymously delivers resources for entities at risk. This study has several boundaries. Constellations of predictive words often do not represent causal mechanisms, and the findings are correlational. However, in enlightening, what people think, feel, and do social media capture sensitive, cognitive, behavioural and environmental indications that have substantial Predictive Analytics that to be validates and are otherwise rationally elusive to researchers and clinicians.
People’s character, mental state, and health behaviours are all reflected in their social media and all have a tremendous impact on health. This blog is to show that language on social media can predict diagnoses within people’s health record, revealing new prospects to personalize care and understand how patients’ ordinary daily lives relate to their health.
Learn More
- Social Media and Health Care Professionals: Benefits, Risks, and Best Practices, 2015, C. Lee Ventola
- The wisdom of patients: Health care meets online social media, 2018, Jane Kahn
- Empowering patients through social media: The benefits and challenges, 2015, Andre Kushniruk
- Harnessing the cloud of patient experience: using social media to detect poor quality healthcare, Felix Greaves, Daniel Ramirez-Cano, Christopher Millett, Ara Darzi, Liam Donaldson




 Previous Post
Previous Post Next Post
Next Post