Analyses for Logistics & Transportation: How Statswork experience enhance L&T operations
Introduction:
In recent decades, Logistics and Transportation facing many challenges that are integrated with e-commerce, data from sensors, GPS, and other devices. Generally, data generating from these sources are tremendously high, and manipulating and handling data for analysis purposes is a tedious one. To overcome these demerits, there are several analytical tools and software available to concise the analysis process for huge data such as Big data analysis, Machine Learning algorithms, Data Science techniques and methodologies, and Artificial Intelligence algorithms and patterns.
With the concern of these emerging technologies, we can successfully do Logistics and Transportation analytics. Hereby this article will lend you to drive effective analytics for Logistics and Transportations. [1]
Logistics & Transportation:
The shipment or transportation of manufactured goods from source to end-user is termed transportation. The management of inward and outward manufactured goods is termed Logistics. The actual role of Logistics is to obtaining, producing and distributing the right products with the right quality to the end-users. Logistics leads to the successful way to plan and manage the storage of goods and distributing those stored products to the market at the right time using proper transport options. Logistics and transportation are in contrast to each other. The roles and responsibilities of Logistics and Transportation managers are different. The managers and higher officials of Logistics have to concentrate on decision-making strategy in packaging the products, containerization, and documentation of product packed details, regulations and protocols for importing and exporting, also focused on risk assessments, vendor and partner communications. [2]
Transportation might differ from Logistics, the movement of manufactured goods from the source to end-user via rail, road, air, sea and space or pipeline. The roles and responsibilities of transportation manager is to make decisions based on the transporting features, goods lifetime while transporting from one source to another destination. [3]
Analytics For Logistics & Transportation:
The purpose of analytics in logistics and transportation is to make the organization in a successful way to prioritize the logistics operation in the organization to promote the goods to the end-users rapidly. It is applicable to transportation analytics also. Based on the analyses, the organization can figure out the user’s insights, market trends, and supply and demand values, lacks of delivery of the products, estimated delivery, user or customer satisfaction. These parameters are primary to run the logistics and transportation based organizations.
There are certain techniques for both logistics and transportation analytics that can induce the sales and increase the supply chain flow. [4]
- Transportation efficiency analysis: To measure the average efficiency of movement of shipments form source to destination.
- Turnaround time: Consumption of time for loading the goods, reloading to the transportation, restocks, fuel details to reach the destination.
- Freight and shipment zone: Estimating how the shipment occurring from source to destination through the transportation and how it reaches the destination.
- Financial management: To manage the financial status based on logistics and transportation cost of th organization and managing the losses if any occurs.
- Operational performance management: To track and monitor all the operations that occur in logistics and transportation processes.
- Sales and Marketing: Analyzing the customer insights based on data extraction and supplying the stocks to the markets. [5]
Enhancing Logistics & Transportation:
Statswork will support for all kind of analytical methodologies and techniques using emerging technologies such as Machine Learning, IoT, Artificial Intelligence, Data Science and Deep learning with experienced and well-knowledge expertise who are certified professionals. All the research process will be done successfully with expertise team who are equipped with tool and software knowledge in analytics also good at programming languages.
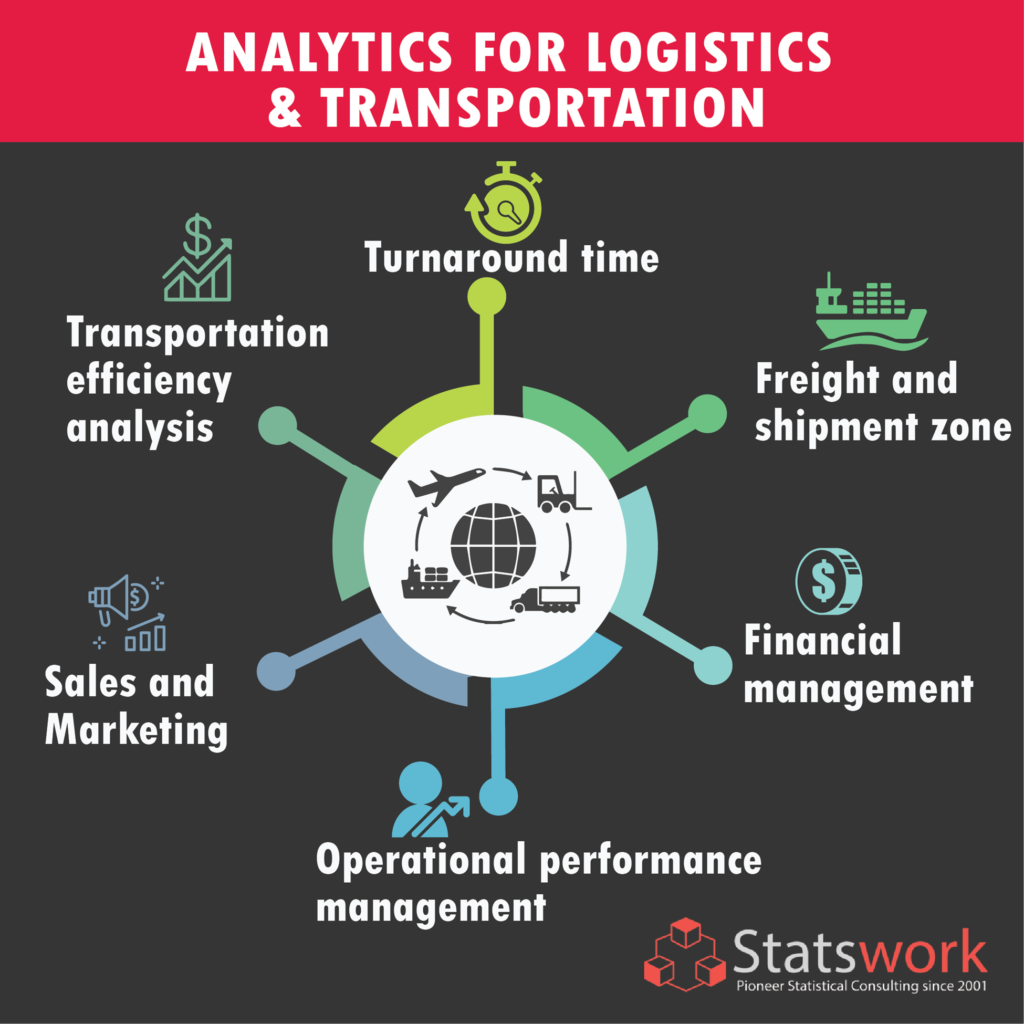
FIGURE: Impact of different end-haulage operations on cost competitiveness [6]
Conclusion:
Supply chain and logistics is a huge area that is becoming increasingly relevant in today’s world of multinational industry and goods, where products manufactured in one country are assembled and shipped in another and consumed in yet another. Any economy’s backbone is transportation, manufacturing, logistics, supply chain, warehousing, management system, and production planning.
The logistics sector is undergoing a period of rapid and unforeseen change. Innovation and technology will pave the way for the future of logistics. Ideas like 3D printing, the Internet of Things (IoT), drone transport, and virtual reality became science fiction not long before.
Future Scope: [6]
- As the automation and data ruling the past two decades, the data can be automatically manipulated in the future to reduce the time consuming process and reduce the man power.
- Comparatively, the emerging technologies are at the gun point to deliver the accurate results and outcomes for all kind of analysis processes.
- Many ongoing process are there to automate and minimize the manpower in supply chain industry.
References:
- Ayed, Abdelkarim Ben, Mohamed Ben Halima, and Adel M. Alimi. “Big data analytics for logistics and transportation.” 2015 4th International Conference on Advanced Logistics and Transport (ICALT). IEEE, 2015.
- Park, Hong Gyun, and Yong Joo Lee. “The efficiency and productivity analysis of large logistics providers services in Korea.” The Asian Journal of Shipping and Logistics 31.4 (2015): 469-476.
- Humayun, Mamoona, et al. “Emerging smart logistics and transportation using IoT and blockchain.” IEEE Internet of Things Magazine 3.2 (2020): 58-62.
- Liu, Chang, et al. “Iot based laundry services: an application of big data analytics, intelligent logistics management, and machine learning techniques.” International Journal of Production Research 58.17 (2020): 5113-5131.
- Kowald, Matthias, and EgilsGinters. “Visual Analytics in Mobility, Transportation and Logistics.” ICTE in Transportation and Logistics 2019 (2020): 82.
- Golpîra, Hêriş, Syed Abdul Rehman Khan, and SinaSafaeipour. “A review of logistics internet-of-things: Current trends and scope for future research.” Journal of Industrial Information Integration (2021): 100194.

 Previous Post
Previous Post