Various ways during which Analytics help Enterprises drive Business Growth
Introduction
Business Analytics help in extracting necessary information from all the data available to transform into a coherent structure for further use. The process of data implementing the advanced analytics techniques in the business domain to derive and predict useful decisions is called BA.
Emergence of the new concept of Tech-Business-Analytics (TBA):
It is the mechanism by which organisations use statistical tools and technology to examine historical data to attain new insights and improve strategic decision-making. It needs managerial skill that integrates business experience, recognises market value opportunities, or recognises problems, with a great understanding of analytical techniques required to align technical talent with functional managers to drive business change. A new model industry 4.0 technology is founded on business analytics using a recently developed analysis framework called predictive analysis [7].
Predictive analytics: This uses statistics and network analytics to forecast future models. Predictive business analytics uses various statistical techniques to build predictive models that extract data from databases, detect trends, and include a predictive score for a range of organisational outcomes. It uses quantitative techniques (e.g., propensity, segmentation, network analysis and econometric forecasting) and technology (such as models and rule-systems) that use past data for the future.
Predictive analytics generates information from historically available datasets to determine and predict future trends and outcomes. The predictive analysis system encompasses 4 steps:
- Gathering data on present trends
- Develop postulates based on present trends
- Generate argument based description
- Predict the future.
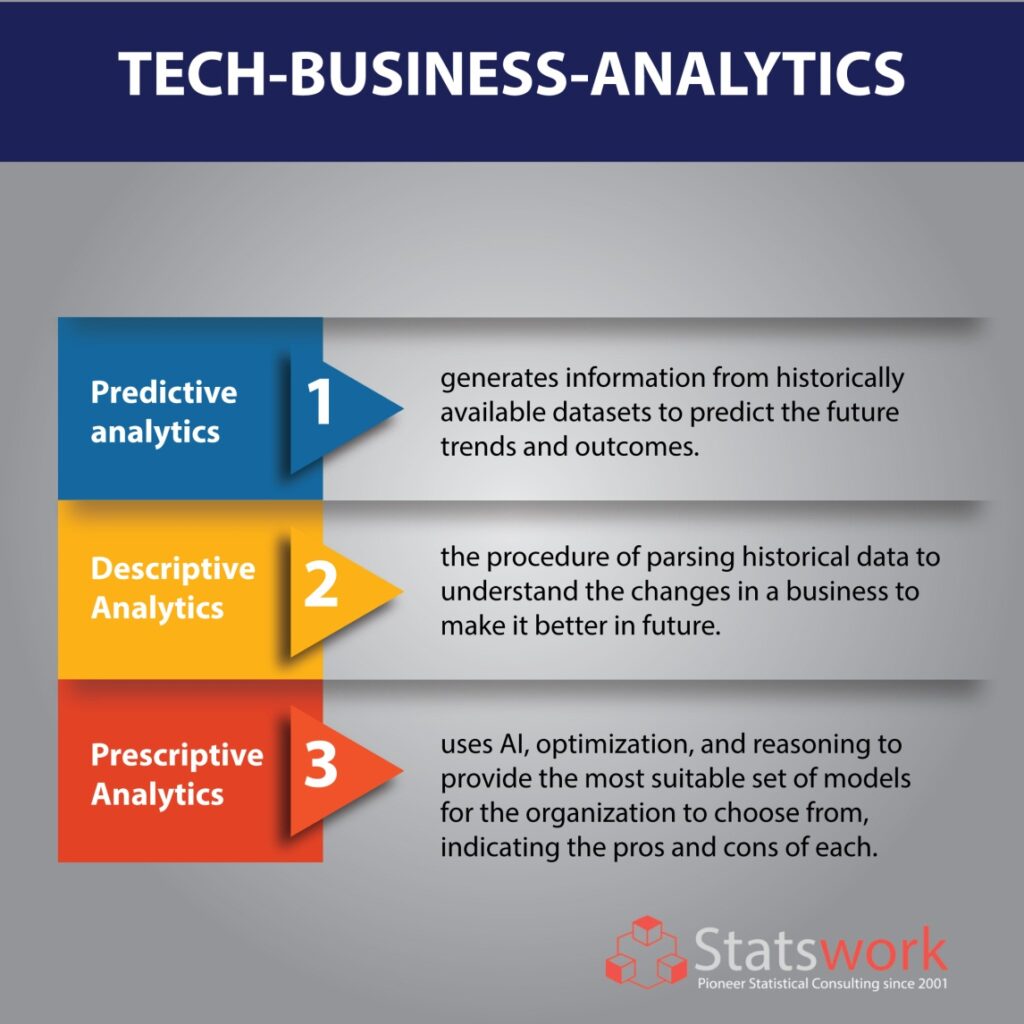
Descriptive Analytics (DESCBA): This uses data mining, data intelligence and web analytics to present the trending information of the near past and current events, helping business models know the demands and drawbacks of the markets.
It provides access to historical and current data. It provides the ability to alert, explore and report using both internal and external data from various sources.
- Descriptive analytics is the procedure of parsing historical data to understand the changes in a business to make it better in future.
- Using a range of historical data and benchmarking, decision-makers obtain a holistic view of performance and trends to base business strategy.
- Descriptive analytics can help to recognise the areas of strength and weakness in an organisation.
- Examples of metrics used in descriptive analytics comprise year-over-year pricing modifications, the number of users, month-over-month sales growth, or the overall revenue per subscriber.
- Descriptive analytics is used inonjuction with newer analytics, such as predictive and prescriptive analytics.
- In its elementry form,of descriptive analytics answers the question, “What happened?”
A mixture of a descriptive-analytical process that provides insight into what happened and a predictive analytical process that provides insight into what might happen helps users predict what will happen, when it will happen and why [8].
Prescriptive Analytics (PREBA): This uses AI, optimization, and reasoning to provide the most suitable set of models for the organization to choose from, indicating the pros and cons of each.
These layers also contain two interconnected analytics: Inquisitive analytics and Preemptive Analytics. The inquisitive analytics uses statistical and factor analysis to approve/reject prepositions, while the combination of three layers is essential for the proper functioning and application of Business analytics architecture.[5]
Conclusion
The analysis conducted by most published studies shows that IoT has massive potential on businesses across many sectors. The data collected from IoT implementation allows businesses to increase productivity, which benefits sales and marketing, resource management, growth potential, and profitability. Since many applications can be accessed on mobile devices, IoT makes users’ day-to-day activities much more convenient. It also helps with inventory management, tracking product use, and tracking sales rates and locations.
References
- Mutuku, M., & Muathe, S. M. (2020). Nexus Analysis: Internet of Things and Business Performance. International Journal of Research in Business and Social Science (2147-4478), 9(4), 175-181.
- Brous, P., Janssen, M., & Herder, P. (2020). The dual effects of the Internet of Things (IoT): A systematic review of the benefits and risks of IoT adoption by organisations. International Journal of Information Management, 51, 101952.
- Grubor, A., & Jakša, O. (2018). Internet marketing as a business necessity. Interdisciplinary Description of Complex Systems: INDECS, 16(2), 265-274.
- Abdel-Basset, M., Mohamed, M., Chang, V., & Smarandache, F. (2019). IoT and its impact on the electronics market: A powerful decision support system for helping customers in choosing the best product. Symmetry, 11(5), 611.
- Shrivastava, G., Peng, S. L., Bansal, H., Sharma, K., & Sharma, M. (Eds.). (2020). New age analytics: transforming the Internet through machine learning, IoT, and trust modeling. CRC Press.
- Hansen, E. B., & Bøgh, S. (2021). Artificial intelligence and Internet of things in small and medium-sized enterprises: A survey. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 58, 362-372.
- Aithal, P. S., & Aithal, S. (2019). New Directions in Scholarly Research–Some Fearless Innovations & Predictions for 21st Century Research. International Journal of Management, Technology, and Social Sciences (IJMTS), 4(1), 1-19.
- Sachin Kumar, S., Dube, D., & Aithal, P. S. (2020). Emerging Concept of Tech-Business-Analytics an Intersection of IoT & Data Analytics and its Applications on Predictive Business Decisions. International Journal of Applied Engineering and Management Letters (IJAEML),(2020), 4(2), 200-210.

 Previous Post
Previous Post Next Post
Next Post